 Planet-hunters have discovered two "super-Earths" orbiting two nearby Sun-like stars. These rocky planets are larger than the Earth but much smaller than ice giants such as Uranus and Neptune.
Planet-hunters have discovered two "super-Earths" orbiting two nearby Sun-like stars. These rocky planets are larger than the Earth but much smaller than ice giants such as Uranus and Neptune.Scientists say the discoveries are a step towards finding potentially habitable planets - smaller planets that are comparable to the Earth. Details of the new planets are described in two papers in the Astrophysical Journal.
More...

 Science Glance
Science Glance The genome of a domestic horse has been successfully sequenced by an international team of researchers. The work, published in the journal Science, may shed light on how horses were domesticated.
The genome of a domestic horse has been successfully sequenced by an international team of researchers. The work, published in the journal Science, may shed light on how horses were domesticated. People chatting on mobile phones are oblivious to their surroundings and can pose a risk to themselves and others, scientists have claimed. Researchers made the discovery by watching the movements of hundreds of people as they crossed a university campus.
People chatting on mobile phones are oblivious to their surroundings and can pose a risk to themselves and others, scientists have claimed. Researchers made the discovery by watching the movements of hundreds of people as they crossed a university campus. European astronomers have found 32 new planets outside our solar system, adding evidence to the theory that the universe has many places where life could develop.
European astronomers have found 32 new planets outside our solar system, adding evidence to the theory that the universe has many places where life could develop. The first results from Nasa's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (Ibex) spacecraft have shown unexpected features at our Solar System's edge.
The first results from Nasa's Interstellar Boundary Explorer (Ibex) spacecraft have shown unexpected features at our Solar System's edge. The National Museum of Natural History announced Wednesday that it is dedicating a new hall to the story of human evolution, giving emphasis not only to how we became humans but how changes in the natural world affected human development.
The National Museum of Natural History announced Wednesday that it is dedicating a new hall to the story of human evolution, giving emphasis not only to how we became humans but how changes in the natural world affected human development.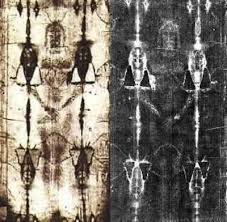 Scientists have reproduced the Shroud of Turin— revered as the cloth that covered Jesus in the tomb — and say the experiment proves the relic was man-made, a group of Italian debunkers claimed Monday.
Scientists have reproduced the Shroud of Turin— revered as the cloth that covered Jesus in the tomb — and say the experiment proves the relic was man-made, a group of Italian debunkers claimed Monday.






























